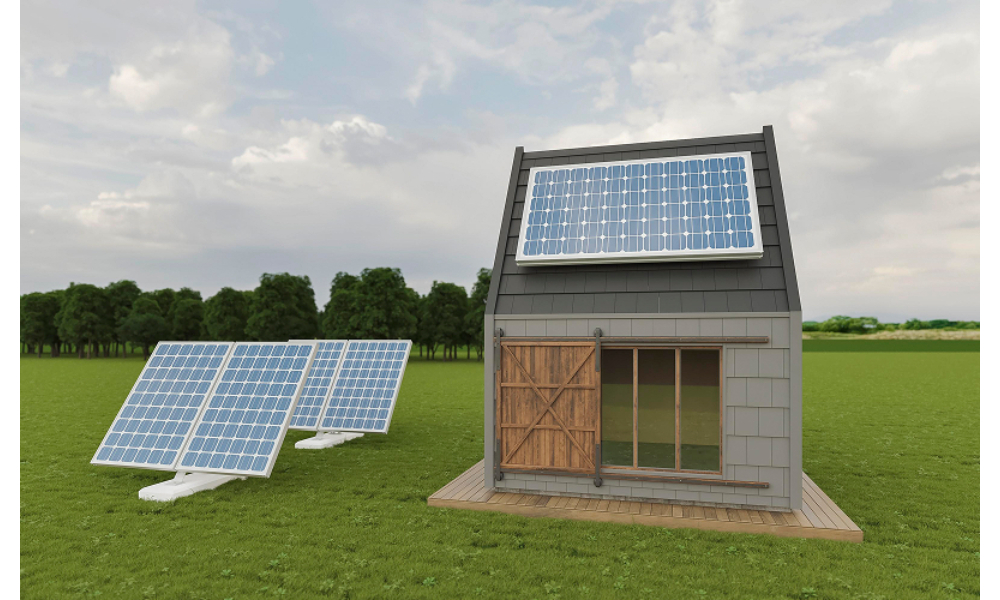
As the demand for renewable energy continues to rise, homeowners and developers are exploring new ways to integrate solar technology into building design. Solar installations are no longer limited to traditional panels. A newer option, solar power roof tiles, is gaining attention for its aesthetic appeal and functional integration. But when it comes to sustainability, how do solar power roof tiles measure up against the traditional solar panel roof?
Manufacturing and Materials
The sustainability of any solar technology begins at the manufacturing stage. Traditional solar panel roofs are typically made from silicon-based photovoltaic (PV) cells mounted on aluminium frames. These components require significant energy to produce, but the process has become more efficient over time. Solar power roof tiles, on the other hand, are designed to blend into the structure of the roof and serve as both a power generator and a roofing material.
This dual-purpose nature can reduce the need for separate roofing materials, which helps offset some of the embedded emissions from their production. However, manufacturing solar power roof tiles tends to be more complex and energy-intensive than producing standard panels. Therefore, while tiles may use fewer additional materials, their production process currently has a higher energy footprint.
Energy Efficiency and Output
Sustainability also depends on how much clean energy each system can generate over its lifespan. Traditional solar panels are known for their efficiency. They are usually positioned at optimal angles for sunlight exposure and can be installed in large arrays, making them highly productive. These systems have been tested extensively and refined to deliver reliable energy under various weather conditions.
Solar power roof tiles, although improving in design, generally have lower energy efficiency than conventional panels. Because they are fixed in line with the roof’s slope, they may not always receive direct sunlight. As a result, solar panel roof tiles typically generate more electricity using the same roof space, making it a more energy-productive choice in most settings.
Installation and Structural Integration
The installation process influences sustainability through labour, material waste, and long-term performance. Traditional solar panels are mounted on top of an existing roof, which adds extra weight and may require structural adjustments. The installation can usually be completed in a short timeframe, and existing roof components remain in place.
Solar power roof tiles replace part or all of the roof during construction or renovation. This approach eliminates the need for separate shingles or tiles, reducing waste if installed as part of a new build. However, retrofitting these tiles onto an existing structure is more complicated, often requiring a complete roof replacement. This increases material waste and carbon output during the installation phase unless it coincides with necessary re-roofing.
Lifespan and Durability
Durability directly impacts sustainability by influencing how often materials need to be replaced. A high-quality solar panel roof can last 25 to 30 years, with some degradation in efficiency over time. Panels are modular and relatively easy to replace or upgrade as needed.
Solar power roof tiles are integrated into the structure, making maintenance more challenging. If a single tile fails, accessing and replacing it may require removing surrounding components. This can lead to higher labour and material costs over the system’s life. While roof tiles are built to withstand weather, their long-term durability is still being evaluated against decades of real-world use.
Learn More: A Guide to Installing Solar Panels in Your Household
End-of-Life Recycling
At the end of their useful life, solar panels and tiles must be recycled to reduce environmental impact. Traditional panels have an established recycling process for glass, silicon, and metals. Although recycling infrastructure is still developing, the industry has made progress in managing panel waste responsibly.
Recycling solar power roof tiles presents more challenges. Due to their construction and integration into roofing systems, separating useful materials is complex. This could hinder their sustainability profile unless recycling technology for integrated systems improves significantly.
Cost and Energy Payback Time
Cost does not directly equate to sustainability, but it does affect how widely a solution is adopted. Traditional solar panel roofs are more affordable and accessible, which increases adoption rates and overall environmental benefits. Their energy payback time, how long it takes to generate the energy used in production, is typically between one and four years.
Solar power roof tiles are expensive to produce and install. Their energy payback period tends to be longer due to lower efficiency and higher initial inputs. While they do serve dual functions, the return on investment in terms of energy sustainability is currently lower than that of traditional panels.
For more information about solar panels in Singapore, contact LHN Energy today.